ATMPlace: Analytical Thermo-Mechanical-Aware Placement Framework for 2.5D-IC
By Qipan Wang, Tianxiang Zhu, Tianyu Jia , Yibo Lin , Runsheng Wang , Ru Huang
Peking University, China
Abstract
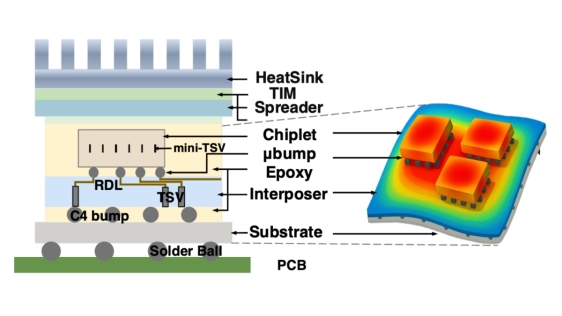
 Rising demand in AI and automotive applications is accelerating 2.5D-IC adoption, with multiple chiplets tightly placed to enable high-speed interconnects and heterogeneous integration. As chiplet counts grow, traditional placement tools—limited by poor scalability and reliance on slow simulations—must evolve beyond wirelength minimization to address thermal and mechanical reliability, critical challenges in heterogeneous integration.
Rising demand in AI and automotive applications is accelerating 2.5D-IC adoption, with multiple chiplets tightly placed to enable high-speed interconnects and heterogeneous integration. As chiplet counts grow, traditional placement tools—limited by poor scalability and reliance on slow simulations—must evolve beyond wirelength minimization to address thermal and mechanical reliability, critical challenges in heterogeneous integration.
In this paper, we present ATMPlace, the first analytical placer for 2.5D-ICs that jointly optimizes wirelength, peak temperature, and operational warpage using physics-based compact models. It generates Pareto-optimal placements for systems with dozens of chiplets. Experimental results demonstrate superior performance: 146% and 52% geo-mean wirelength improvement over TAP-2.5D and TACPlace, respectively, with 3–13% lower temperature and 5–27% less warpage — all achieved ∼10× faster. The proposed framework is general and can be extended to enable fast, scalable, and reliable design exploration for next-generation 2.5D systems.
Index Terms — 2.5D-IC; Thermo-Mechanical Optimization; Chiplet Placement; Thermal Warpage
To read the full article, click here
Related Chiplet
- DPIQ Tx PICs
- IMDD Tx PICs
- Near-Packaged Optics (NPO) Chiplet Solution
- High Performance Droplet
- Interconnect Chiplet
Related Technical Papers
- ATPlace2.5D: Analytical Thermal-Aware Chiplet Placement Framework for Large-Scale 2.5D-IC
- STAMP-2.5D: Structural and Thermal Aware Methodology for Placement in 2.5D Integration
- LaZagna: An Open-Source Framework for Flexible 3D FPGA Architectural Exploration
- ATSim: A Fast and Accurate Simulation Framework for 2.5D/3D Chiplet Thermal Design Optimization
Latest Technical Papers
- Link Quality Aware Pathfinding for Chiplet Interconnects
- Effects of Poor Workload Partitioning on System Performance for Chiplet-Based Systems
- Mozart: Modularized and Efficient MoE Training on 3.5D Wafer-Scale Chiplet Architectures
- Network Design for Wafer-Scale Systems with Wafer-on-Wafer Hybrid Bonding
- CarbonPATH: Carbon-aware pathfinding and architecture optimization for chiplet-based AI systems