REX: A Remote Execution Model for Continuos Scalability in Multi-Chiplet-Module GPUs
By Mario Ibáñez Bolado, Borja Perez Pavón, Jose Luis, Bosque Orero
Department of Computer Engineering and Electronics, Universidad de Cantabria, Spain
Abstract
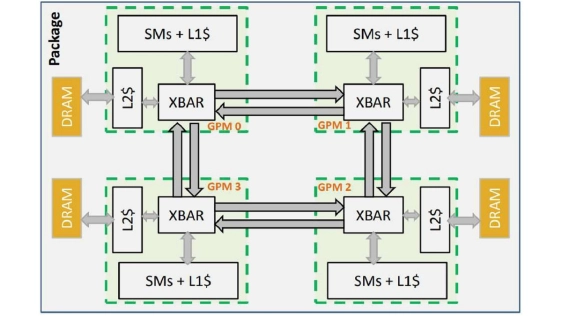
 Monolithic GPU architectures face growing limitations due to power density, yield issues, and manufacturing complexity, motivating a shift toward multi-chiplet designs. While promising, these architectures struggle with workloads exhibiting irregular memory access patterns, where static data placement is often insufficient. Though data locality can help, it does not adapt well to dynamic access behaviour, leading to performance degradation. This paper introduces REX, a runtime mechanism that migrates threads to the chiplet where their data resides, adapting dynamically to the generated memory access patterns with a fine granularity. By relocating computation instead of data, REX improves locality and minimises remote memory accesses, which are especially costly in multi-chiplet environments. As a result, it reduces inter-chiplet traffic and scales efficiently with the number of chiplets. On irregular workloads, the solution demonstrates consistent performance gains, averaging a 13% speedup, with improvements reaching up to 38%. Moreover, its scalability with chiplet count is particularly noteworthy, delivering a 25% average gain, and peaking at an impressive 84% in the most favourable scenarios.
Monolithic GPU architectures face growing limitations due to power density, yield issues, and manufacturing complexity, motivating a shift toward multi-chiplet designs. While promising, these architectures struggle with workloads exhibiting irregular memory access patterns, where static data placement is often insufficient. Though data locality can help, it does not adapt well to dynamic access behaviour, leading to performance degradation. This paper introduces REX, a runtime mechanism that migrates threads to the chiplet where their data resides, adapting dynamically to the generated memory access patterns with a fine granularity. By relocating computation instead of data, REX improves locality and minimises remote memory accesses, which are especially costly in multi-chiplet environments. As a result, it reduces inter-chiplet traffic and scales efficiently with the number of chiplets. On irregular workloads, the solution demonstrates consistent performance gains, averaging a 13% speedup, with improvements reaching up to 38%. Moreover, its scalability with chiplet count is particularly noteworthy, delivering a 25% average gain, and peaking at an impressive 84% in the most favourable scenarios.
Keywords: GPU, Multi-Chiplet, Multi-GPU, Parallel Programming, Thread Migration
To read the full article, click here
Related Chiplet
- DPIQ Tx PICs
- IMDD Tx PICs
- Near-Packaged Optics (NPO) Chiplet Solution
- High Performance Droplet
- Interconnect Chiplet
Related Technical Papers
- Fault Modeling, Testing, and Repair for Chiplet Interconnects
- Fast and Accurate Jitter Modeling for Statistical BER Analysis for Chiplet Interconnect and Beyond
- Occamy: A 432-Core 28.1 DP-GFLOP/s/W 83% FPU Utilization Dual-Chiplet, Dual-HBM2E RISC-V-based Accelerator for Stencil and Sparse Linear Algebra Computations with 8-to-64-bit Floating-Point Support in 12nm FinFET
- Leveraging Chiplet-Locality for Efficient Memory Mapping in Multi-Chip Module GPUs
Latest Technical Papers
- Link Quality Aware Pathfinding for Chiplet Interconnects
- Effects of Poor Workload Partitioning on System Performance for Chiplet-Based Systems
- Mozart: Modularized and Efficient MoE Training on 3.5D Wafer-Scale Chiplet Architectures
- Network Design for Wafer-Scale Systems with Wafer-on-Wafer Hybrid Bonding
- CarbonPATH: Carbon-aware pathfinding and architecture optimization for chiplet-based AI systems