Optimizing Attention on GPUs by Exploiting GPU Architectural NUMA Effects
By Mansi Choudhary 1, Karthik Sangaiah 2, Sonali Singh 2, Muhammad Osama 2, Lisa Wu Wills 3, Ganesh Dasika 2
1 Department of ECE, Duke University, Durham, USA
2 Advanced Micro Devices Inc., Santa Clara, USA
3 Department of Computer Science, Duke University, Durham, USA
Abstract
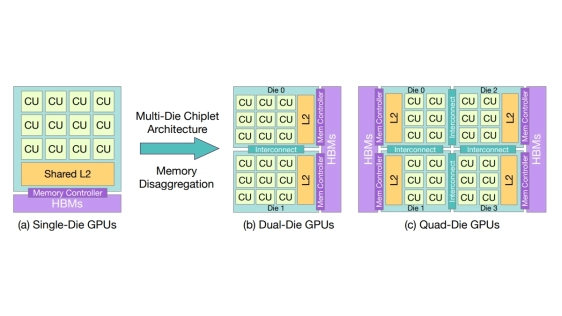
 The rise of disaggregated AI GPUs has exposed a critical bottleneck in large-scale attention workloads: non-uniform memory access (NUMA). As multi-chiplet designs become the norm for scaling compute capabilities, memory latency and bandwidth vary sharply across compute regions, undermining the performance of traditional GPU kernel scheduling strategies that assume uniform memory access. We identify how these NUMA effects distort locality in multi-head attention (MHA) and present Swizzled Head-first Mapping, a spatially-aware scheduling strategy that aligns attention heads with GPU NUMA domains to exploit intra-chiplet cache reuse. On AMD's MI300X architecture, our method achieves up to 50% higher performance over state-of-the-art attention algorithms using conventional scheduling techniques and sustains consistently high L2 cache hit rates of 80-97%. These results demonstrate that NUMA-aware scheduling is now fundamental to achieving full efficiency on next-generation disaggregated GPUs, offering a path forward for scalable AI training and inference.
The rise of disaggregated AI GPUs has exposed a critical bottleneck in large-scale attention workloads: non-uniform memory access (NUMA). As multi-chiplet designs become the norm for scaling compute capabilities, memory latency and bandwidth vary sharply across compute regions, undermining the performance of traditional GPU kernel scheduling strategies that assume uniform memory access. We identify how these NUMA effects distort locality in multi-head attention (MHA) and present Swizzled Head-first Mapping, a spatially-aware scheduling strategy that aligns attention heads with GPU NUMA domains to exploit intra-chiplet cache reuse. On AMD's MI300X architecture, our method achieves up to 50% higher performance over state-of-the-art attention algorithms using conventional scheduling techniques and sustains consistently high L2 cache hit rates of 80-97%. These results demonstrate that NUMA-aware scheduling is now fundamental to achieving full efficiency on next-generation disaggregated GPUs, offering a path forward for scalable AI training and inference.
To read the full article, click here
Related Chiplet
- DPIQ Tx PICs
- IMDD Tx PICs
- Near-Packaged Optics (NPO) Chiplet Solution
- High Performance Droplet
- Interconnect Chiplet
Related Technical Papers
- Leveraging Chiplet-Locality for Efficient Memory Mapping in Multi-Chip Module GPUs
- REX: A Remote Execution Model for Continuos Scalability in Multi-Chiplet-Module GPUs
- Quantum Dot DBR Lasers Monolithically Integrated on Silicon Photonics by In-Pocket Heteroepitaxy
- LaZagna: An Open-Source Framework for Flexible 3D FPGA Architectural Exploration
Latest Technical Papers
- Spatiotemporal thermal characterization for 3D stacked chiplet systems based on transient thermal simulation
- Interconnect-Aware Logic Resynthesis for Multi-Die FPGAs
- Scope: A Scalable Merged Pipeline Framework for Multi-Chip-Module NN Accelerators
- Scaling Routers with In-Package Optics and High-Bandwidth Memories
- TDPNavigator-Placer: Thermal- and Wirelength-Aware Chiplet Placement in 2.5D Systems Through Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning