Hybrid surface pre-treatments for enhancing copper-to-copper direct bonding
By Wei-Ting Chen 1, Liang-Hsing Shih 2, Kiyokazu Yasuda 3, Jenn-Ming Song 1,2,3,4
1 National Chung Hsing University, Nantou City, Nantou County 540216, Taiwan
2 National Chung Hsing University, Taichung 402, Taiwan
3 Osaka University, Osaka 565-0817, Japan
4 National Chung Hsing University, Taichung 402, Taiwan
Abstract
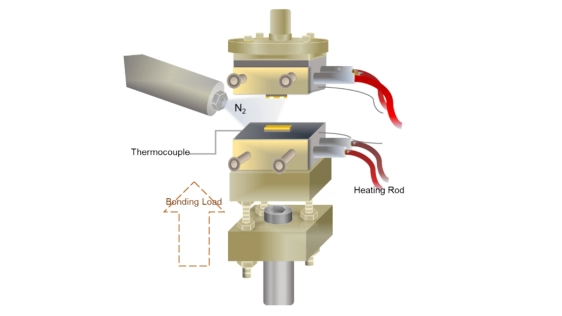
 Three-dimensional integrated circuits (3D IC) require low-temperature, high-reliability Cu–Cu direct bonding to support fine-pitch vertical interconnects and heterogeneous integration. This study developed a hybrid surface pretreatment method combining plasmas and pulsed high-energy flash irradiations to modify Cu surface conditions and enhance bonding performance. Sputtered Cu films were treated using various plasma gases (N2 and those with different H2 contents up to 30%), followed by flash exposure, and their effects on surface energy, stress evolution, and joint strength were systematically evaluated. N2 plasma activated Cu surface and gave rise to the formation of a stable Cu4N layer that effectively inhibited oxidation. Subsequent flash exposure caused compressive stress, which accelerated Cu atom diffusion and advanced the bonding. Hydrogen-containing plasmas further activated Cu surface, promoted the hydrophilicity and improved joint strength. However, the extremely activated surface thus formed is susceptible to excessive oxidation in the following flash light exposure. It can be proposed that for achieving robust joint strength the oxide thickness on the Cu surface should be controlled less than 7 nm. These findings highlight that reliable bonding can be achieved by controlling the combined effects of surface activation, oxidation and stresses introduced during pretreatment.
Three-dimensional integrated circuits (3D IC) require low-temperature, high-reliability Cu–Cu direct bonding to support fine-pitch vertical interconnects and heterogeneous integration. This study developed a hybrid surface pretreatment method combining plasmas and pulsed high-energy flash irradiations to modify Cu surface conditions and enhance bonding performance. Sputtered Cu films were treated using various plasma gases (N2 and those with different H2 contents up to 30%), followed by flash exposure, and their effects on surface energy, stress evolution, and joint strength were systematically evaluated. N2 plasma activated Cu surface and gave rise to the formation of a stable Cu4N layer that effectively inhibited oxidation. Subsequent flash exposure caused compressive stress, which accelerated Cu atom diffusion and advanced the bonding. Hydrogen-containing plasmas further activated Cu surface, promoted the hydrophilicity and improved joint strength. However, the extremely activated surface thus formed is susceptible to excessive oxidation in the following flash light exposure. It can be proposed that for achieving robust joint strength the oxide thickness on the Cu surface should be controlled less than 7 nm. These findings highlight that reliable bonding can be achieved by controlling the combined effects of surface activation, oxidation and stresses introduced during pretreatment.
Keywords: Cu toCu direct bonding, Surface activation, Plasma, Flash, Oxidation
To read the full article, click here
Related Chiplet
- DPIQ Tx PICs
- IMDD Tx PICs
- Near-Packaged Optics (NPO) Chiplet Solution
- High Performance Droplet
- Interconnect Chiplet
Related Technical Papers
- Temporary Direct Bonding by Low Temperature Deposited SiO2 for Chiplet Applications
- Ammonia Plasma Surface Treatment for Enhanced Cu–Cu Bonding Reliability for Advanced Packaging Interconnection
- Probing the Nanoscale Onset of Plasticity in Electroplated Copper for Hybrid Bonding Structures via Multimodal Atomic Force Microscopy
- Revamping the Semiconductor Industry with Hybrid Bonding
Latest Technical Papers
- Spatiotemporal thermal characterization for 3D stacked chiplet systems based on transient thermal simulation
- Interconnect-Aware Logic Resynthesis for Multi-Die FPGAs
- Scope: A Scalable Merged Pipeline Framework for Multi-Chip-Module NN Accelerators
- Scaling Routers with In-Package Optics and High-Bandwidth Memories
- TDPNavigator-Placer: Thermal- and Wirelength-Aware Chiplet Placement in 2.5D Systems Through Multi-Agent Reinforcement Learning